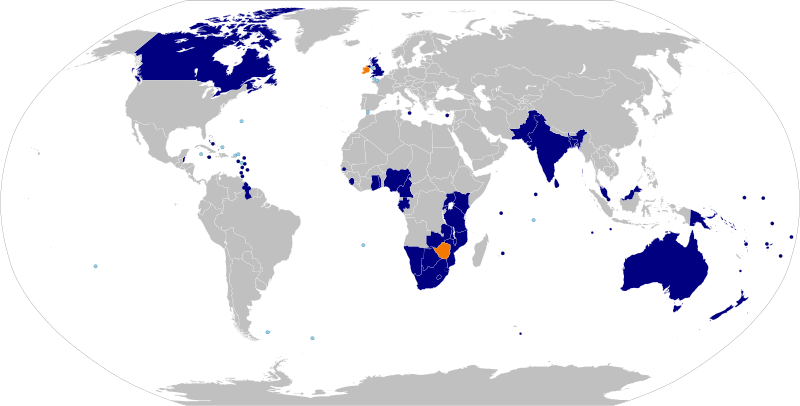
The Commonwealth of Nations, commonly known as the Commonwealth (formerly the British Commonwealth),[1] is an intergovernmental organisation of 53 member states that were mostly territories of the former British Empire. The Commonwealth operates by intergovernmental consensus of the member states, organised through the Commonwealth Secretariat, and non-governmental organisations, organised through the Commonwealth Foundation.
The Commonwealth dates back to the mid 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which established the member states as "free and equal". The symbol of this free association is Queen Elizabeth II who is the Head of the Commonwealth. The Queen is also the monarch of 16 members of the Commonwealth, known as Commonwealth realms. The other members of the Commonwealth have different persons as head of state: 32 members are republics and five members are monarchies with a different monarch.
Member states have no legal obligation to one another. Instead, they are united by language, history, culture, and their shared values of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law. These values are enshrined in the Commonwealth Charter and promoted by the quadrennial Commonwealth Games. On 3 October 2013, after 48 years of membership, Gambia became the most recent nation to withdraw from the Commonwealth.
The Commonwealth covers more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), almost a quarter of the world land area, and spans all the continents. With an estimated population of 2.328 billion, near a third of the world population, the Commonwealth in 2014 produced a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of $10.45 trillion, representing 17% of the gross world product when measured in purchasing power parity (PPP) and 14% of the gross world product when measured nominally.
History
Origin
In 1884, while visiting Australia, Lord Rosebery described the changing British Empire, as some of its colonies became more independent, as a "Commonwealth of Nations". Conferences of British and colonial prime ministers occurred periodically from the first one in 1887, leading to the creation of the Imperial Conferences in 1911.
The Commonwealth developed from the Imperial Conferences. A specific proposal was presented by Jan Smuts in 1917 when he coined the term "the British Commonwealth of Nations" and envisioned the "future constitutional relations and readjustments in essence" at the all-important Versailles Conference of 1919 by delegates from the dominions as well as Britain. The term first received imperial statutory recognition in the Anglo-Irish Treaty of 1921, when the term "British Commonwealth of Nations" was substituted for "British Empire" in the wording of the oath taken by members of parliament of the Irish Free State.
Dominions
In the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, Britain and its dominions agreed they were "equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs, though united by common allegiance to the Crown, and freely associated as members of the British Commonwealth of Nations." These aspects to the relationship were formalised by the Statute of Westminster in 1931, which applied to Canada without the need for ratification, but Australia, New Zealand, and Newfoundland had to ratify the statute for it to take effect. Newfoundland never did, as on 16 February 1934, with the consent of its parliament, the government of Newfoundland voluntarily ended and governance reverted to direct control from London. Newfoundland later joined Canada as its 10th province in 1949. Australia and New Zealand ratified the Statute in 1942 and 1947 respectively.
After World War II ended, the British Empire was gradually dismantled to the 14 British overseas territories still held by the United Kingdom. In April 1949, following the London Declaration, the word "British" was dropped from the title of the Commonwealth to reflect its changing nature. Burma (also known as Myanmar, 1948) and Aden (1967) are the only states that were British colonies at the time of the war not to have joined the Commonwealth upon independence. Former British protectorates and mandates that did not become members of the Commonwealth are Egypt (independent in 1922), Iraq (1932), Transjordan (1946), British Palestine (part of which became the state of Israel in 1948), Sudan (1956), British Somaliland (which united with the former Italian Somaliland in 1960 to form the Somali Republic), Kuwait (1961), Bahrain (1971), Oman (1971), Qatar (1971), and the United Arab Emirates (1971).
Republics
On 18 April 1949, Ireland formally became a republic in accordance with the Irish Republic of Ireland Act 1948. Because it did this, it was automatically excluded from the Commonwealth. While Ireland had not actively participated in the Commonwealth since the early 1930s and was content to leave the Commonwealth, other dominions wished to become republics without losing Commonwealth ties. The issue came to a head in April 1949 at a Commonwealth prime ministers' meeting in London. Under the London Declaration, India agreed that, when it became a republic in January 1950, it would accept the British Sovereign as a "symbol of the free association of its independent member nations and as such the Head of the Commonwealth". Upon hearing this, King George VI told the Indian politician Krishna Menon: "So, I've become 'as such'". The other Commonwealth countries recognised India's continuing membership of the association. At Pakistan's insistence, India was not regarded as an exceptional case and it was assumed that other states would be accorded the same treatment as India.
The London Declaration is often seen as marking the beginning of the modern Commonwealth. Following India's precedent, other nations became republics, or constitutional monarchies with their own monarchs, while some countries retained the same monarch as the United Kingdom, but their monarchies developed differently and soon became fully independent of the British monarchy. The monarch is regarded as a separate legal personality in each realm, even though the same person is monarch of each realm.
New Commonwealth
As the Commonwealth grew, Britain and the pre-1945 dominions became informally known as the Old Commonwealth and planners in the interwar period, like Lord Davies, who had also taken "a prominent part in building up the League of Nations Union" in the United Kingdom, in 1932 founded the New Commonwealth Society, of which Winston Churchill became the president. This new society was aimed at the creation of an international air force to be the arm of the League of Nations, to allow nations to disarm and safeguard the peace.
The term New Commonwealth has been used in Great Britain (especially in the 1960s and 1970s) to refer to recently decolonised countries, predominantly non-white and developing. It was often used in debates about immigration from these countries.
Plan G and inviting Europe to join
At a time when Germany and France, together with Belgium, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands, were planning for what later became the European Union, and newly independent African countries were joining the Commonwealth, new ideas were floated to prevent Britain from becoming isolated in economic affairs. British trade with the Commonwealth was four times larger than trade with Europe. The British government under Prime Minister Anthony Eden considered in 1956-57 a "plan G" to create a European free trade zone while also protecting the favoured status of the Commonwealth. Britain also considered inviting Scandinavian and other European countries to join the Commonwealth so it would become a major economic common market. At one point in October 1956 Eden and French Prime Minister Guy Mollet discussed having France join the Commonwealth. Nothing came of any of the proposals.
Structure

Head of the Commonwealth
Under the formula of the London Declaration, Queen Elizabeth II is the Head of the Commonwealth, a title that is by law a part of Elizabeth's royal titles in each of the Commonwealth realms, the 16 members of the Commonwealth that recognise the Queen as their monarch. However, when the monarch dies, the successor to the crown does not automatically become Head of the Commonwealth. The position is symbolic, representing the free association of independent members, the majority of which (32) are republics, and five have monarchs of different royal houses (Brunei, Lesotho, Malaysia, Swaziland, and Tonga).
Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting
The main decision-making forum of the organisation is the biennial Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM), where Commonwealth heads of government, including (amongst others) prime ministers and presidents, assemble for several days to discuss matters of mutual interest. CHOGM is the successor to the Meetings of Commonwealth Prime Ministers and, earlier, the Imperial Conferences and Colonial Conferences, dating back to 1887. There are also regular meetings of finance ministers, law ministers, health ministers, etc. Members in arrears, as special members before them, are not invited to send representatives to either ministerial meetings or CHOGMs.
The head of government hosting the CHOGM is called the Commonwealth Chairperson-in-Office and retains the position until the following CHOGM. After the most recent CHOGM, in Colombo, Sri Lanka, from 10â€"17 November 2013 Sri Lanka's president, Mahinda Rajapaksa, became the Chairperson-in-Office and will continue to hold the title until the next CHOGM in Malta in November 2015.
Commonwealth Secretariat
The Commonwealth Secretariat, established in 1965, is the main intergovernmental agency of the Commonwealth, facilitating consultation and co-operation among member governments and countries. It is responsible to member governments collectively. The Commonwealth of Nations is represented in the United Nations General Assembly by the secretariat as an observer. The secretariat organises Commonwealth summits, meetings of ministers, consultative meetings and technical discussions; it assists policy development and provides policy advice, and facilitates multilateral communication among the member governments. It also provides technical assistance to help governments in the social and economic development of their countries and in support of the Commonwealth's fundamental political values.
The secretariat is headed by the Commonwealth Secretary-General who is elected by Commonwealth heads of government for no more than two four-year terms. The secretary-general and two deputy secretaries-general direct the divisions of the Secretariat. The present secretary-general is Kamalesh Sharma, from India, who took office on 1 April 2008, succeeding Don McKinnon of New Zealand (2000â€"2008), and was re-elected in 2011 to his second term in 2012. The first secretary-general was Arnold Smith of Canada (1965â€"75), followed by Sir Shridath Ramphal of Guyana (1975â€"90) and Chief Emeka Anyaoku of Nigeria (1990â€"99).
Commonwealth citizenship and High Commissioners
In recognition of their shared heritage and culture, Commonwealth countries are not considered to be "foreign" to each other. The exception is Australia, where no such distinction is made - in the High Court case of Sue v Hill, other Commonwealth countries were held to be foreign powers. When engaging bilaterally with one another, Commonwealth governments exchange High Commissioners instead of ambassadors. Between two Commonwealth realms, they represent the Head of Government rather than the Head of State.
In addition, some members treat resident citizens of other Commonwealth countries preferentially to citizens of non-Commonwealth countries. Britain and several others, mostly in the Caribbean, grant the right to vote to Commonwealth citizens who reside in those countries. Some states, such as Canada, Australia and New Zealand, have abolished such preferences. In non-Commonwealth countries in which their own country is not represented, Commonwealth citizens may seek consular assistance at the British embassy. Other alternatives can also occur such as an emergency consular services agreement between Canada and Australia that began in 1986.
Membership
Criteria
The criteria for membership of the Commonwealth of Nations have developed over time from a series of separate documents. The Statute of Westminster 1931, as a fundamental founding document of the organisation, laid out that membership required dominionhood. The 1949 London Declaration ended this, allowing republican and indigenous monarchic members on the condition that they recognised the British monarch as the "Head of the Commonwealth". In the wake of the wave of decolonisation in the 1960s, these constitutional principles were augmented by political, economic, and social principles. The first of these was set out in 1961, when it was decided that respect for racial equality would be a requirement for membership, leading directly to the withdrawal of South Africa's re-application (which they were required to make under the formula of the London Declaration upon becoming a republic). The 14 points of the 1971 Singapore Declaration dedicated all members to the principles of world peace, liberty, human rights, equality, and free trade.
These criteria were unenforceable for two decades, until, in 1991, the Harare Declaration was issued, dedicating the leaders to applying the Singapore principles to the completion of decolonisation, the end of the Cold War, and the end of apartheid in South Africa. The mechanisms by which these principles would be applied were created, and the manner clarified, by the 1995 Millbrook Commonwealth Action Programme, which created the Commonwealth Ministerial Action Group (CMAG), which has the power to rule on whether members meet the requirements for membership under the Harare Declaration. Also in 1995, an Inter-Governmental Group was created to finalise and codify the full requirements for membership. Upon reporting in 1997, as adopted under the Edinburgh Declaration, the Inter-Governmental Group ruled that any future members would have to have a direct constitutional link with an existing member.
In addition to this new rule, the former rules were consolidated into a single document. These requirements are that members must accept and comply with the Harare principles, be fully sovereign states, recognise the monarch of the Commonwealth realms as the Head of the Commonwealth, accept the English language as the means of Commonwealth communication, and respect the wishes of the general population with regard to Commonwealth membership. These requirements had undergone review, and a report on potential amendments was presented by the Committee on Commonwealth Membership at the 2007 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting. New members were not admitted at this meeting, though applications for admission were considered at the 2009 CHOGM.
New members must "as a general rule" have a direct constitutional link to an existing member. In most cases, this is due to being a former colony of the United Kingdom, but some have links to other countries, either exclusively or more directly (e.g. Samoa to New Zealand, Papua New Guinea to Australia, and Namibia to South Africa). The first member to be admitted without having any constitutional link to the British Empire or a Commonwealth member was Mozambique, a former Portuguese colony, in 1995 following its first democratic elections and South Africa's re-admission in 1994. Mozambique's controversial entry led to the Edinburgh Declaration and the current membership guidelines. In 2009, Rwanda became the second Commonwealth member admitted not to have any such constitutional links. It was a Belgian trust territory that had been a German colony until World War I. Consideration for its admission was considered an "exceptional circumstance" by the Commonwealth Secretariat.
Members
The Commonwealth comprises 53 countries, across all six inhabited continents. The members have a combined population of 2.1Â billion people, almost a third of the world population, of which 1.26Â billion live in India and 94% live in Asia and Africa combined. After India, the next-largest Commonwealth countries by population are Pakistan (180Â million), Nigeria (170Â million), Bangladesh (156Â million), the United Kingdom (63Â million) and South Africa (52Â million). Tuvalu is the smallest member, with about 10,000 people.
The land area of the Commonwealth nations is about 31,500,000 km2 (12,200,000 sq mi), or about 21% of the total world land area. The three largest Commonwealth nations by area are Canada at 9,984,670 km2 (3,855,100 sq mi), Australia at 7,617,930 km2 (2,941,300 sq mi), and India at 3,287,263 km2 (1,269,219 sq mi). The Commonwealth members have a combined gross domestic product of over $9 trillion, 78% of which is accounted for by the four largest economies: United Kingdom ($2.4 trillion), Canada ($1.8 trillion), India ($1.8 trillion) and Australia ($1.5 trillion).
The status of "Member in Arrears" is used to denote those that are in arrears in paying subscription dues. The status was originally known as "special membership", but was renamed on the Committee on Commonwealth Membership's recommendation. There are currently no Members in Arrears. The most recent Member in Arrears, Nauru, returned to full membership in June 2011. Nauru has alternated between special and full membership since joining the Commonwealth, depending on its financial situation.
Applicants
In 1997 the Commonwealth Heads of Government agreed that, to become a member of the Commonwealth, an applicant country should, as a rule, have had a constitutional association with an existing Commonwealth member; that it should comply with Commonwealth values, principles and priorities as set out in the Harare Declaration; and that it should accept Commonwealth norms and conventions.
South Sudan is currently (2013) the only country specifically expressing an interest in joining the Commonwealth. Some commentators have suggested that Israel and Palestine have considered applying for membership, but there has been no formal approach."
Other eligible applicants could be any of the remaining inhabited British overseas territories, Crown dependencies, Australian external territories and Associated States of New Zealand if they become fully independent. Many such jurisdictions are already directly represented within the Commonwealth, particularly through the Commonwealth Family. There are also former British possessions that have not become independent, for example, Hong Kong, which still participates in some of the institutions within the Commonwealth Family. All three Crown dependencies regard the existing situation as unsatisfactory and have lobbied for change. The States of Jersey have called on the UK Foreign Secretary to request that the Commonwealth Heads of Government "consider granting associate membership to Jersey and the other Crown Dependencies as well as any other territories at a similarly advanced stage of autonomy". Jersey has proposed that it be accorded "self-representation in all Commonwealth meetings; full participation in debates and procedures, with a right to speak where relevant and the opportunity to enter into discussions with those who are full members; and no right to vote in the Ministerial or Heads of Government meetings, which is reserved for full members". The States of Guernsey and the Government of the Isle of Man have made calls of a similar nature for a more integrated relationship with the Commonwealth, including more direct representation and enhanced participation in Commonwealth organisations and meetings, including Commonwealth Heads of Government Meetings. The Chief Minister of the Isle of Man has said: "A closer connection with the Commonwealth itself would be a welcome further development of the Island's international relationships"
At the time of the Suez Crisis in 1956, in the face of colonial unrest and international tensions, French Prime Minister Guy Mollet proposed to British Prime Minister Anthony Eden that their two countries be joined in a "union". When that proposal was turned down, Mollet suggested that France be allowed to join the Commonwealth, with "a common citizenship arrangement on the Irish basis." In 1957, after both proposals had been rejected, France signed the Treaty of Rome with West Germany and the other founding nations of the Common Market, later to become the European Union (EU), which the United Kingdom joined in 1973. The other European members of the Commonwealth (Malta and Cyprus) joined the EU in 2004.
Suspension
In recent years, the Commonwealth has suspended several members "from the Councils of the Commonwealth" for "serious or persistent violations" of the Harare Declaration, particularly in abrogating their responsibility to have democratic government. This is done by the Commonwealth Ministerial Action Group (CMAG), which meets regularly to address potential breaches of the Harare Declaration. Suspended members are not represented at meetings of Commonwealth leaders and ministers, although they remain members of the organisation. Currently, there are no suspended members.
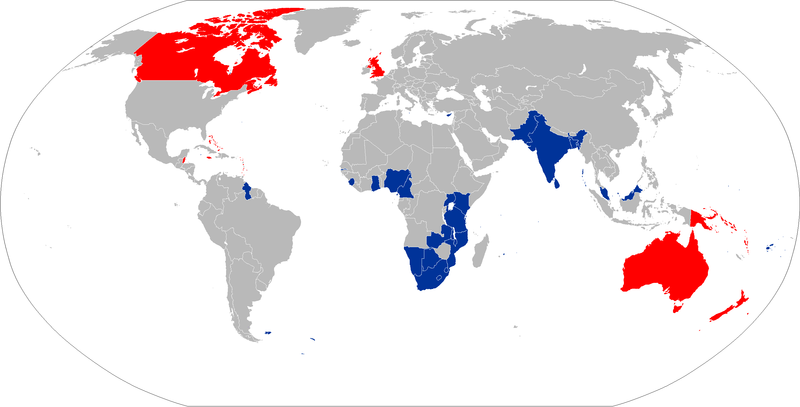
Nigeria was suspended between 11 November 1995 and 29 May 1999, following its execution of Ken Saro-Wiwa on the eve of the 1995 CHOGM. Pakistan was the second country to be suspended, on 18 October 1999, following the military coup by Pervez Musharraf. The Commonwealth's longest suspension came to an end on 22 May 2004, when Pakistan's suspension was lifted following the restoration of the country's constitution. Pakistan was suspended for a second time, far more briefly, for six months from 22 November 2007, when Musharraf called a state of emergency. Zimbabwe was suspended in 2002 over concerns regarding the electoral and land reform policies of Robert Mugabe's ZANU-PF government, before it withdrew from the organisation in 2003.
The declaration of a Republic in Fiji in 1987, after military coups designed to deny Indo-Fijians political power, was not accompanied by an application to remain. Commonwealth membership was held to have lapsed until 1997, after discriminatory provisions in the republican constitution were repealed and reapplication for membership made. Fiji has since been suspended twice, with the first imposed from 6 June 2000 to 20 December 2001 after another coup. Fiji was suspended yet again in December 2006, following the most recent coup. At first, the suspension applied only to membership on the Councils of the Commonwealth. After failing to meet a Commonwealth deadline for setting a date for national elections by 2010, Fiji was "fully suspended" on 1 September 2009. The Secretary-General of the Commonwealth, Kamalesh Sharma, confirmed that full suspension meant that Fiji would be excluded from Commonwealth meetings, sporting events and the technical assistance programme (with an exception for assistance in re-establishing democracy). Sharma stated that Fiji would remain a member of the Commonwealth during its suspension, but would be excluded from emblematic representation by the secretariat. On 19 March 2014 Fiji’s full suspension was amended to a suspension from councils of the Commonwealth by the Commonwealth Ministerial Action Group, permitting Fiji to join a number of Commonwealth activities, including the Commonwealth Games. Fiji's suspension was lifted in September 2014. The Commonwealth Ministerial Action Group fully reinstated Fiji as a member following elections in September 2014.
Most recently, international pressure has been mounting to suspend Sri Lanka from the Commonwealth, citing grave human rights violations by the host country. There were also calls to change the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting 2013 from Sri Lanka to another member country. Canadian prime minister Stephen Harper threatened to boycott the event, but was instead represented at the meeting by Deepak Obhrai. The UK Foreign Affairs Committee called upon Prime Minister David Cameron to boycott the event, however, he chose to attend.
Termination
As membership is purely voluntary, member governments can choose at any time to leave the Commonwealth. Pakistan left on 30 January 1972 in protest at the Commonwealth's recognition of breakaway Bangladesh, but rejoined on 2 August 1989. Zimbabwe's membership was suspended in 2002 on the grounds of alleged human rights violations and deliberate misgovernment, and Zimbabwe's government terminated its membership in 2003. The Gambia left the Commonwealth on 3 October 2013.
Although heads of government have the power to suspend member states from active participation, the Commonwealth has no provision for the expulsion of members. Until 2007, Commonwealth realms that became republics automatically ceased to be members, until (like India in 1950) they obtained the permission of other members to remain in the organisation. This policy has been changed, so if any current Commonwealth realms were to become republics, they would not have to go through this process.
Ireland had withdrawn its participation in the Commonwealth in the 1930s, attending its last Commonwealth governmental heads' meeting in 1932. However it continued to be regarded by the Commonwealth as a Commonwealth member until it declared itself a republic, on 18 April 1949. It is the only country whose membership terminated without any declaration withdrawing from the organisation. Instead, it was (with its own tacit support) excluded from the organisation under the rules then applicable.
South Africa was prevented from continuing as a member after it became a republic in 1961, due to hostility from many members, particularly those in Africa and Asia as well as Canada, to its policy of apartheid. The South African government withdrew its application to remain in the organisation as a republic when it became clear at the 1961 Commonwealth Prime Ministers' Conference that any such application would be rejected. South Africa was re-admitted to the Commonwealth in 1994, following the end of apartheid earlier that year.
The transfer of sovereignty over Hong Kong in 1997 ended the colony's ties to the Commonwealth through the United Kingdom. The government of Hong Kong, as a special administrative region of China, did not pursue membership. Hong Kong has nevertheless continued to participate in some of the organisations of the Commonwealth family, such as the Commonwealth Lawyers Association, the Commonwealth Parliamentary Association, the Association of Commonwealth Universities and the Commonwealth Association of Legislative Counsel.
Politics
Objectives and activities
The Commonwealth's objectives were first outlined in the 1971 Singapore Declaration, which committed the Commonwealth to the institution of world peace; promotion of representative democracy and individual liberty; the pursuit of equality and opposition to racism; the fight against poverty, ignorance, and disease; and free trade. To these were added opposition to discrimination on the basis of gender by the Lusaka Declaration of 1979, and environmental sustainability by the Langkawi Declaration of 1989. These objectives were reinforced by the Harare Declaration in 1991.
The Commonwealth's current highest-priority aims are on the promotion of democracy and development, as outlined in the 2003 Aso Rock Declaration, which built on those in Singapore and Harare and clarified their terms of reference, stating, "We are committed to democracy, good governance, human rights, gender equality, and a more equitable sharing of the benefits of globalisation." The Commonwealth website lists its areas of work as: Democracy, Economics, Education, Gender, Governance, Human Rights, Law, Small States, Sport, Sustainability, and Youth.
Through a separate voluntary fund, Commonwealth governments support the Commonwealth Youth Programme, a division of the Secretariat with offices in Gulu (Uganda), Lusaka (Zambia), Chandigarh (India), Georgetown (Guyana) and Honiara (Solomon Islands).
Competence
In recent years, the Commonwealth has been accused of not being vocal enough on its core values. Allegations of a leaked memo from the Secretary General instructing staff not to speak out on human rights were published in October 2010.
The Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting 2011 considered a report by an Commonwealth Eminent Persons Group panel which asserted that the organisation had lost its relevance and was decaying due to the lack of a mechanism to censure member countries when they violated human rights or democratic norms. The panel made 106 "urgent" recommendations including the adoption of a Charter of the Commonwealth, the creation of a new commissioner on the rule of law, democracy and human rights to track persistent human rights abuses and allegations of political repression by Commonwealth member states, recommendations for the repeal of laws against homosexuality in 41 Commonwealth states and a ban on forced marriage. The failure to release the report, or accept its recommendations for reforms in the area of human rights, democracy and the rule of law, was decried as a "disgrace" by former British Foreign Secretary Sir Malcolm Rifkind, a member of the EPG, who told a press conference: "The Commonwealth faces a very significant problem. It's not a problem of hostility or antagonism, it's more of a problem of indifference. Its purpose is being questioned, its relevance is being questioned and part of that is because its commitment to enforce the values for which it stands is becoming ambiguous in the eyes of many member states. The Commonwealth is not a private club of the governments or the secretariat. It belongs to the people of the Commonwealth."
In the end, two-thirds of the EPG's 106 urgently recommended reforms were referred to study groups, an act described by one EPG member as having them "kicked into the long grass". There was no agreement to create the recommended position of human rights commissioner, instead a ministerial management group was empowered with enforcement: the group includes alleged human rights offenders. It was agreed to develop a charter of values for the Commonwealth without any decision on how compliance with its principles would be enforced.
The result of the effort was that a new Charter of the Commonwealth was signed by Queen Elizabeth on 11 March 2013 at Marlborough House, which opposes "all forms of discrimination, whether rooted in gender, race, colour, creed, political belief or other grounds".
Elections
- Elections are also scheduled to be held in Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Brunei, Cyprus, Dominica, Fiji (suspended), Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Kiribati, Maldives, Malta, Mauritius, Nauru, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Singapore, Samoa, Seychelles, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu. In accordance with the Westminster system these nations' next general elections have no fixed date, but must be held within a specified term length, usually four of five years.
Economy
Internal market
Although the Commonwealth does not have a common market, research by the Royal Commonwealth Society has shown that trade with another Commonwealth member is up to 50% more than with a non-member on average. Some politicians in the United Kingdom have proposed that there should be a Commonwealth free trade zone, with some suggesting it as an alternative to its membership in the European Union.
Commonwealth Family
Commonwealth countries share many links outside government, with over a hundred Commonwealth-wide non-governmental organisations, notably for sport, culture, education, law and charity. The Association of Commonwealth Universities is an important vehicle for academic links, particularly through scholarships, principally the Commonwealth Scholarship, for students to study in universities in other Commonwealth countries. There are also many non-official associations that bring together individuals who work within the spheres of law and government, such as the Commonwealth Lawyers Association and the Commonwealth Parliamentary Association.
Commonwealth Foundation
The Commonwealth Foundation is an intergovernmental organisation, resourced by and reporting to Commonwealth governments, and guided by Commonwealth values and priorities. Its mandate is to strengthen civil society in the achievement of Commonwealth priorities: democracy and good governance, respect for human rights and gender equality, poverty eradication and sustainable, people-centred and sustainable development, and to promote arts and culture.
The Foundation was established in 1965 by the Heads of Government. Admittance is open to all members of the Commonwealth, and in December 2008, stood at 46 out of the 53 member countries. Associate Membership, which is open to associated states or overseas territories of member governments, has been granted to Gibraltar. 2005 saw celebrations for the Foundation's 40th Anniversary. The Foundation is headquartered in Marlborough House, Pall Mall, London. Regular liaison and co-operation between the Secretariat and the Foundation is in place. The Foundation continues to serve the broad purposes for which it was established as written in the Memorandum of Understanding.
Commonwealth Games
The Commonwealth Games, a multi-sport event, is held every four years; the 2010 Commonwealth Games were held in New Delhi, India, and the 2014 Commonwealth Games in Glasgow, Scotland, and the 2018 Commonwealth Games will be on Gold Coast, Australia. As well as the usual athletic disciplines, as at the Summer Olympic Games, the games include sports particularly popular in the Commonwealth, such as bowls, netball, and rugby sevens. Started in 1930 as the Empire Games, the games were founded on the Olympic model of amateurism, but were deliberately designed to be "the Friendly Games", with the goal of promoting relations between Commonwealth countries and celebrating their shared sporting and cultural heritage.
The games are the Commonwealth's most visible activity and interest in the operation of the Commonwealth increases greatly when the Games are held. There is controversy over whether the gamesâ€"and sport generallyâ€"should be involved in the Commonwealth's wider political concerns. The 1977 Gleneagles Agreement was signed to commit Commonwealth countries to combat apartheid through discouraging sporting contact with South Africa (which was not then a member), whilst the 1986 games were boycotted by most African, Asian, and Caribbean countries for the failure of other countries to enforce the Gleneagles Agreement.
Commonwealth War Graves Commission
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) is responsible for maintaining the war graves of 1.7Â million service personnel that died in the First and Second World Wars fighting for Commonwealth member states. Founded in 1917 (as the Imperial War Graves Commission), the Commission has constructed 2,500 war cemeteries, and maintains individual graves at another 20,000 sites around the world. The vast majority of the latter are civilian cemeteries in Great Britain. In 1998, the CWGC made the records of its buried online to facilitate easier searching.
Commonwealth war cemeteries often feature similar horticulture and architecture, with larger cemeteries being home to a Cross of Sacrifice and Stone of Remembrance. The CWGC is notable for marking the graves identically, regardless of the rank, country of origin, race, or religion of the buried. It is funded by voluntary agreement by six Commonwealth members, in proportion to the nationality of the casualties in the graves maintained, with 75% of the funding coming from Britain.
Commonwealth of Learning
The Commonwealth of Learning (COL) is an intergovernmental organisation created by the Heads of Government to encourage the development and sharing of open learning/distance education knowledge, resources and technologies. COL is helping developing nations improve access to quality education and training.
Commonwealth Business Council
The Commonwealth Business Council (CBC) was formed at 1997 CHOGM. The aim was to utilise the global network of the Commonwealth more effectively for the promotion of global trade and investment for shared prosperity. The CBC acts as a bridge for co-operation between business and government, concentrating efforts on these specific areas enhancing trade, facilitating ICT for Development, mobilising investment, promoting corporate citizenship, and public-private partnerships. The CBC has a dedicated team, CBC Technologies, based in London and is focused on the international technology and global services industry throughout the Commonwealth.
Culture
Many Commonwealth nations possess traditions and customs that are elements of a shared Commonwealth culture. Examples include common sports such as cricket and rugby, driving on the left, the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy, common law, widespread use of the English language, designation of English as an official language, military and naval ranks, and the use of British rather than American spelling conventions (see English in the Commonwealth of Nations).
Sport
Many Commonwealth nations play similar sports that are considered quintessentially "British" in character, rooted in and developed under British rule or hegemony, including football, cricket, rugby, and netball. This has led to the development of friendly national rivalries between the main sporting nations that have often defined their relations with each another. Indeed, said rivalries preserved close ties by providing a constant in international relationships, even as the Empire transformed into the Commonwealth. Externally, playing these sports is seen to be a sign of sharing a certain Commonwealth culture; the adoption of cricket at schools in Rwanda is seen as symbolic of the country's move towards Commonwealth membership.
Besides the Commonwealth Games, other sporting competitions are organised on a Commonwealth basis, through championship tournaments such as the Commonwealth Taekwondo Championships, Commonwealth Fencing Championships, Commonwealth Judo Championships, Commonwealth Rowing Championships, Commonwealth Sailing Championships, Commonwealth Shooting Championships and Commonwealth Pool Lifesaving Championships. The Commonwealth Boxing Council has long maintained Commonwealth titles for the best boxers in the Commonwealth.
Literature
The shared history of British presence has produced a substantial body of writing in many languages, known as Commonwealth literature. The Association for Commonwealth Literature and Language Studies, with nine chapters worldwide and an international conference is held every three years.
In 1987, the Commonwealth Foundation established the annual Commonwealth Writers' Prize "to encourage and reward the upsurge of new Commonwealth fiction and ensure that works of merit reach a wider audience outside their country of origin". Prizes are awarded for the best book and best first book in the Commonwealth, as well as regional prizes for the best book and best first book from each of four regions. Although not officially affiliated with the Commonwealth, the prestigious Man Booker Prize is awarded annually to an author from a Commonwealth country or the three former members, Ireland, Zimbabwe, and the Gambia. This honour is one of the highest in literature.
Political system
Due to their shared constitutional histories, most countries in the Commonwealth have similar legal and political systems. The Commonwealth requires its members to be functioning democracies that respect human rights and the rule of law. Half of Commonwealth countries have the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. The Commonwealth Parliamentary Association facilitates co-operation between legislatures across the Commonwealth, and the Commonwealth Local Government Forum promotes good governance amongst local government officials. Most Commonwealth members use common law, modelled on English law. The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council is the supreme court of 14 Commonwealth members.
Symbols
The Commonwealth has adopted a number of symbols that represent the association of its members. The English language is recognised as a symbol of the members' heritage; as well as being considered a symbol of the Commonwealth, recognition of it as "the means of Commonwealth communication" is a prerequisite for Commonwealth membership.
The flag of the Commonwealth consists of the symbol of the Commonwealth Secretariat, a gold globe surrounded by emanating "rays", on a dark blue field; it was designed for the second CHOGM in 1973, and officially adopted on 26 March 1976. 1976 also saw the organisation agree to a common date on which to commemorate Commonwealth Day, the second Monday in March, having developed separately on different dates from Empire Day celebrations.
Recognition
In 2009, to mark the 60th anniversary of the founding of the Commonwealth, the Royal Commonwealth Society commissioned a poll of public opinion in seven of the member states: Australia, Canada, India, Jamaica, Malaysia, South Africa and the United Kingdom. It found that most people in these countries were largely ignorant of the Commonwealth's activities, aside from the Commonwealth Games, and indifferent toward its future. Support for the Commonwealth was twice as high in developing countries as in developed countries; it was lowest in Great Britain.
See also
- Anglosphere
- Commonwealth
- English-speaking world
- List of economic communities
- Representatives of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Propaganda in the Rhodesian Bush War
- Community of Portuguese Language Countries, an equivalent grouping of Portuguese-speaking countries and territories
- Commonwealth of Independent States, a grouping of Post-Soviet states outside the European Union
Notes
- 1. ^ The Commonwealth of Nations is sometimes called the "British Commonwealth" to differentiate it from the Commonwealth of Independent States, also called the "Russian Commonwealth". However, the title "British Commonwealth", along with "British Empire", is historic and should not be used to describe the modern Commonwealth of Nations.
References
Further reading
- N Mansergh, The Commonwealth in the World, University of Toronto Press, 1982. ISBN 0-8020-2492-0.
- R J Moore, Making the New Commonwealth, Clarendon Press, 1988. ISBN 0-19-820112-5.
- (French) C A Auplat, Les ONG du Commonwealth contemporain: rôles, bilans et perspectives, L'Harmattan, Paris, 2003. ISBN 2-7475-5513-5.
- Timothy M Shaw, Commonwealth: Inter- and Non-State Contributions to Global Governance, Routledge, 2008. ISBN 978-0-415-35120-1 (hbk); ISBN 978-0-415-35121-8 (pbk).
- K C Wheare, The Constitutional Structure of the Commonwealth, Clarendon Press, 1960. ISBN 0-313-23624-0.
- W D McIntyre, A Guide to the Contemporary Commonwealth, Palgrave, 2001. ISBN 0-333-96310-5.
External links
- Media related to Commonwealth of Nations at Wikimedia Commons
- Commonwealth Secretariat
- Commonwealth Foundation
- Commonwealth English Literature Forum







0 komentar :
Posting Komentar